About blood types
Every person has a blood type (O, A, B, or AB) and an Rh factor, either positive or negative. The blood type and the Rh factor simply mean that a person's blood has certain specific features. The blood type is found as proteins on red blood cells and in body fluids. The Rh factor is a protein that is found on the covering of the red blood cells. If the Rh factor protein is on the cells, the person is Rh-positive. If there is no Rh factor protein, the person is Rh- negative.
The following are the possible combinations of blood types with the Rh factors:
|
Blood Type
|
A
|
B
|
O
|
AB
|
|
Rh positive
|
A+
|
B+
|
O+
|
AB+
|
|
Rh negative
|
A-
|
B-
|
O-
|
AB-
|
Rh factors are genetically determined. A baby may have the blood type and Rh factor of either parent or a combination of both parents. Rh factors follow a common pattern of genetic inheritance. The Rh-positive gene is dominant (stronger) and, even when paired with an Rh-negative gene, the positive gene takes over:
-
If a person has the genes + +, the Rh factor in the blood will be positive.
-
If a person has the genes + -, the Rh factor will also be positive.
-
If a person has the genes - -, the Rh factor will be negative.
A baby receives one gene from the father and one from the mother. More specifically, consider the following:
If a father's Rh factor genes are + +, and the mother's are + +, the baby will have one + from the father and one + gene from the mother. The baby will be + + Rh positive.
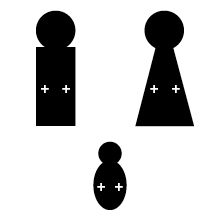
If a father's Rh factor genes are + +, and the mother's are - -, the baby will have one + from the father and one - gene from the mother. The baby will be + - Rh-positive.
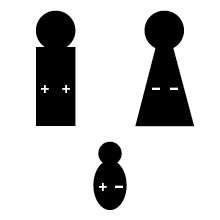
If the father's genes are + - Rh-positive, and the mother's are + - Rh-positive, the baby can be:
-
+ + Rh-positive
-
+ - Rh-positive
-
- - Rh-negative
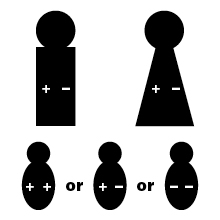
If the father's genes are - -, and the mother's are + -, the baby can be
-
+ - Rh-positive
-
- - Rh-negative
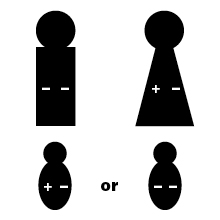
If the father's genes are - -, and the mother's are - -, the baby will be:
Problems with the Rh factor happen when the mother's Rh factor is negative and the baby's is positive. If the mother hasn't already been sensitized to Rh positive blood, they may be given Rh immunoglobulin. This will prevent being sensitized if the baby is Rh positive. Sometimes an incompatibility may happen when the mother is blood type O and the baby is either A or B. This can affect the newborn baby, who may need treatment after birth.